A scale is a unified collection of notes-which any addition is heard to be extraneous and a selection which is in some sense complete.
the scale must also fulfil the functions demanded of it. There are three principal functions that a scale may be asked to fufil:
- to serve as a harmonic resource
- to be tonally effective
- to serve as a melodic resource
Major scale- The major scale has triads which can be represented numerically as: one, ii, iii IV, vi and Vii which are chords or as 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 which are notes.
Between the 7th and 8th degrees and also the 3rd and 4th degrees there are semitones, between all the other adjacent notes there are whole tones. The major scale is strongly effective at producing a tonic function on the major chord that is built on its home note.
Minor scale- the minor scale is well used for classical music, this where it is well know. for minor mode music it is known to be the harmonic foundation. with a minor scale the sixth degree is raised to the seventh by a chromatic semitone. these devices are he ones that transforms the augmented second into a major second.
Aeolian mode- in a aeolian mode there are semitones between the 2nd, 3rd, 5th and 6th degrees, and leaving whole Tones between all the other degrees. Its cadences are less decisive than the harmonic minor scales so it is generally avoided in the classical music.
Clefs- Clefs are placed on a Grand Staff. The top part of a Grand Staff is called the Treble Clef and The lower half of the Grand staff is called the Bass Clef. Notes appear on a Bass Clef and a Treble Clef. Treble clefs are placed above middle Cs on the piano and Bass clefs are placed below middle C on the piano.
The sharp sign means to play the next key to the right.
The flat sign means to play the next key to the left.
Dynamic signs tells you how loudly or softly to play a piano.
Natural signs cancel a sharp or flat.
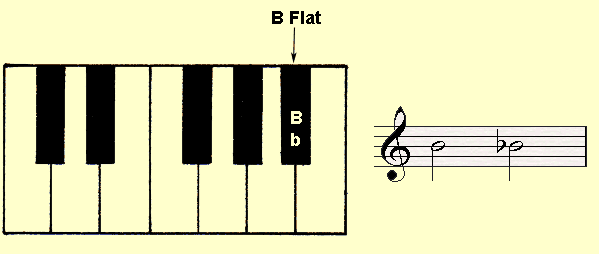 FLAT signs
FLAT signs
 SHARP signs
SHARP signs
 NATURAL signs
NATURAL signs
 DYNAMIC signs
DYNAMIC signs
 This is a grand staff.
This is a grand staff.

No comments:
Post a Comment